
Ethereum supporters may have heard of EVM, or Ethereum Virtual Machine, but blockchain advocates on other blockchains may not have. The EVM is one of the foundations of the Ethereum network and how it operates. It is essential for carrying out transactions and can literally be referred to as a virtual machine as the name suggests.
Not quite clear on what it means yet? Don’t worry, let’s dive into more detail.
Table of Contents
- What is an EVM? | Benefits and All You Need to Know
What is EVM?
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a network consisting of thousands of interconnected computers and can be viewed as a giant decentralized computer. The Ethereum Virtual Machine is responsible for housing accounts on the Ethereum network. The EVM has the computational function for all projects on Ethereum.
What is The Ethereum Virtual Machine for?
Ethereum is the initial blockchain that introduced smart contracts and programmability for them. The EVM is not only the part of the blockchain for executing smart contracts, but it is also where developers create decentralized apps (dApps) and ensures a seamless experience for users on the distributed ledger.
The EVM is used by every Ethereum node to preserve blockchain consensus.
How the EVM Works
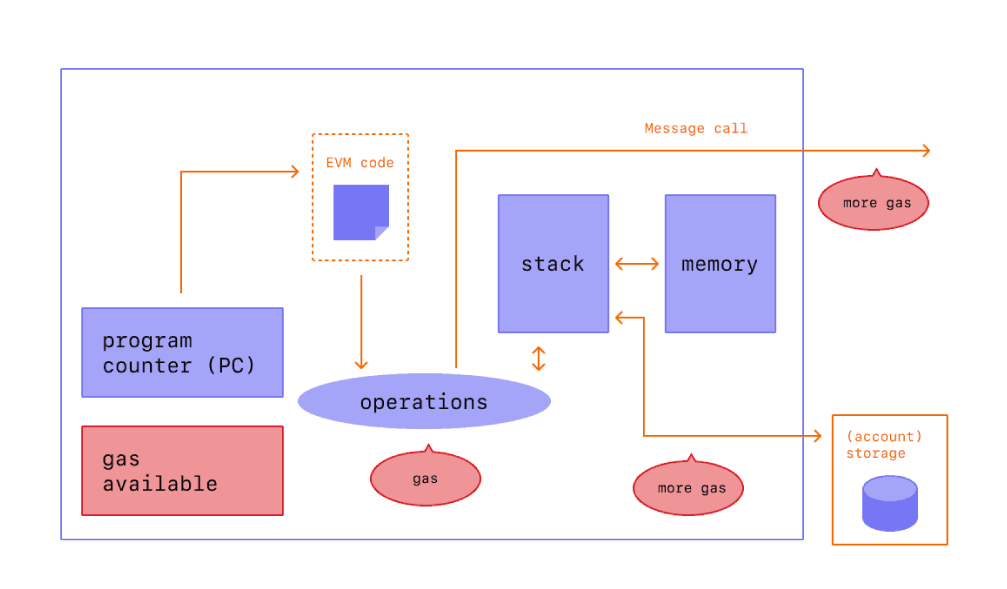
Napster, LimeWire, BitTorrent, these are more rudimentary examples of the Ethereum Virtual Machine. Once a file is uploaded onto these platforms for others to download and share, it is nearly impossible for authorities to wipe out all the files at once without extracting and deleting from every single computer that’s linked to the platforms individually.
Image Source: https://ethereum.org/
The EVM was introduced to scale this decentralized network. The Ethereum Virtual Machine is a facilitator between the computers and the code, carrying out transactions and supporting the Solidity programming language.
The EVM can be run at any location in the world and it can accommodate different operating systems and hardware. The Ethereum Virtual Machine can be seen as the heart of the entire operation, making sure everything is running seamlessly and without downtime.
Pros and Cons of the Ethereum Virtual Machine
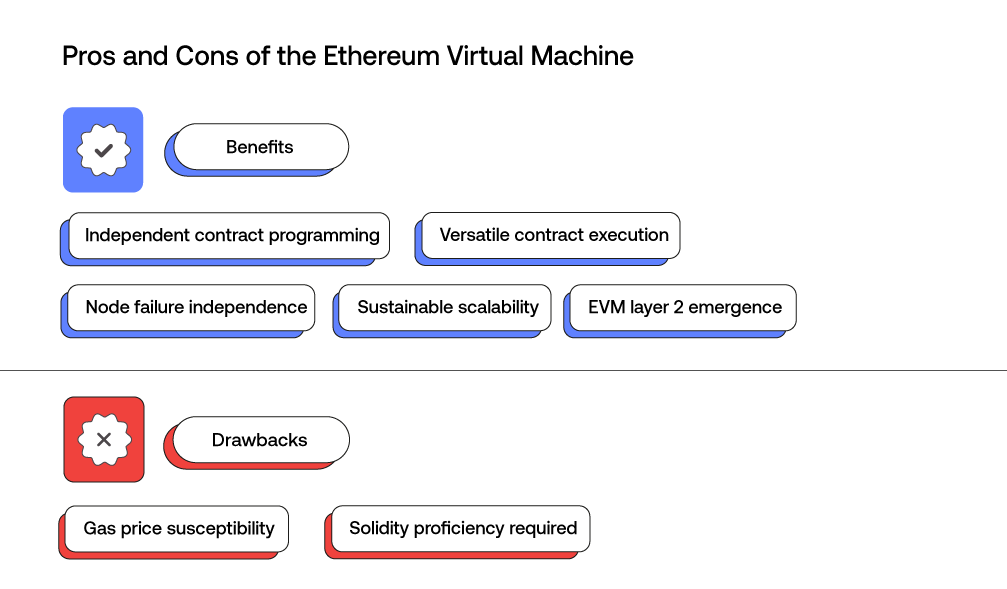
The Ethereum Virtual Machine sounds like something that only produces advantages for the Ethereum blockchain such as aiding in smart contract deployment and ensuring consensus on the Ethereum blockchain. Although it does provide indisputable benefits, there are some drawbacks as well.
Benefits
- Developers can program code without worrying about the impact to the rest of the blockchain
- Can run smart contracts in various computing environments and maintain consensus
- A single node failure does not impact the rest of the smart contracts or dApp
- Sustainable scalability
- More and more EVM-compatible layer 2 blockchain technology emerging
Drawbacks
- The Ethereum Virtual machine is not immune to the high gas prices on the blockchain when executing smart contracts and other transactions
- Solidity is the prominent programming language on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (although smart contracts are compatible with multiple programming languages such as Vyper, and Yul) so developers need to be adept at it.
The Future of the Ethereum Virtual Machine
Although the Ethereum Virtual Machine was conceptualized back in 2013 by Ethereum’s founder, Vitalik Buterin, there is still a lot of potential for growth. There is no debate that the impact the EVM has had so far has largely been positive, gas fees were quite an issue in the beginning.
Since the EVM is revolutionary tech and cross-chain interoperability is so important right now within the ecosystem, many EVM-compatible blockchains have emerged reporting to be cheaper and faster than Ethereum.
While this may have been true, since The Merge in 2022 (Ethereum’s overhaul into the proof-of-stake consensus), we may see even more improvements from Ethereum.
FAQ
What powers the Ethereum Virtual Machine?
The Ethereum Virtual Machine is powered by gas on the blockchain. It requires gas to execute smart contracts and other transactions on the Ethereum system.
What are some EVM-compatible blockchains?
Some examples of EVM-compatible blockchains aside from Ethereum are Binance Smart Chain (BSC), Polygon, Avalanche, Fantom.
Conclusion
Think of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) as a master program that is responsible for the execution of all smaller programs such as individual smart contracts. The EVM ensures smooth operation within the distributed ledger. It’s safe to say that it is a breakthrough in cross-chain interoperability, with much room for future growth and optimization.
Related Articles:
- The Ethereum Virtual Machine for Beginners
- SecuX Crypto Wallets Add 300+ EVM Chains Support
- What is Gas on Ethereum?
0 comments