Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as financial advice.
Without giving away too much info, data tokenization is a cornerstone in the cryptocurrency and blockchain world by bringing unprecedented security and efficiency to users. The term is relatively new, especially for crypto beginners and those trying to understand the tech and concepts in web3.
Let's take a deeper dive into what exactly data tokenization entails and what it can do for data security.
Table of Contents
- Data Tokenization Answered
- Data Tokenization’s Role in Data Security
- Techniques of Data Tokenization
- Secure Hash
- Format Preserving
- Split Tokenization
- Randomized Tokenization
- Cryptographic
- Detokenization
- Data Tokenization VS Data Encryption
- Pros and Cons of Data Tokenization
- Conclusion
Data Tokenization Answered
Data tokenization is a sophisticated process that provides a robust solution to enhance security and streamline transactions. It involves the conversion of sensitive information into unique tokens, rendering the original data practically indecipherable to unauthorized users and entities. These tokens are often generated through complex algorithms and serve as digital representations of the original data.
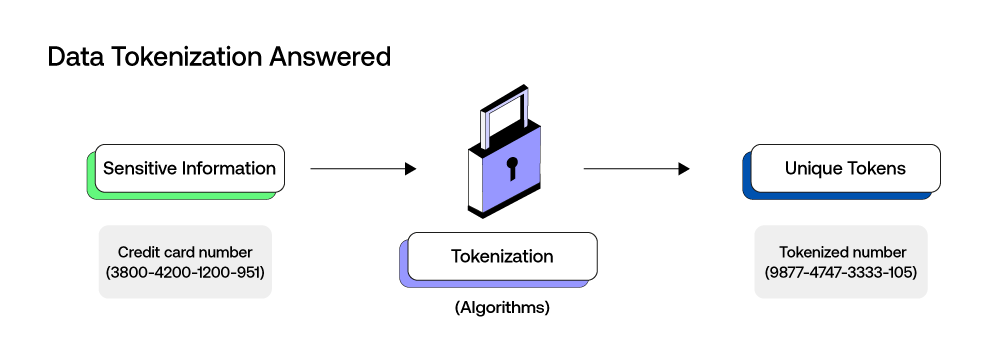
The key is the tokens lack inherent meaning without the proper decryption keys. Pertaining to cryptocurrency, this technique is instrumental in protecting sensitive user information, such as personal IDs and financial data, from security breaches.
Data tokenization greatly lowers the risk of unauthorized access and data leaks. Not only does data tokenization strengthen the security of digital assets but it also fosters increased efficiency in transaction processes.
Some examples of what data tokenization can protect include sensitive cardholder data, and personally identifiable information like your name, address and phone number.
Data Tokenization’s Role in Data Security
Let's look a little closer at what the tokenization process of sensitive data can provide in terms of security.
Data Protection
By transforming sensitive information into tokens, tokenization helps protect the original data from unauthorized access. This process ensures a robust defense against potential security issues, making sure that users' confidential data remains protected within the cryptographic walls of tokenization.
Risk Mitigation
Data tokenization can also do a lot for reducing online risks. Because the true nature of the original sensitive data is obscured, the potential impact of a data leak is significantly reduced. This approach not only safeguards against financial losses but also shields the reputation of entities involved in cryptocurrency and blockchain transactions.
Data Integrity
Ensuring the integrity of data is of the utmost importance in decentralized systems like blockchains. Through the tokenization process, the original data's integrity is preserved, as tokens maintain a one-to-one relationship with the source information. This means that the data remains unalterable throughout its lifetime, which strengthens the reliability of information within blockchain networks.
Data Handling
Data tokenization streamlines the process of information handling by providing a secure and manageable way to deal with sensitive data. It simplifies data handling protocols, contributing to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of cryptocurrency transactions within the blockchain ecosystem.
Compliance
Lastly, data tokenzation plays a role in compliance as well. Meeting regulatory standards is a critical aspect of any blockchain-based operation, and it also gives users some peace of mind. Data tokenization aligns seamlessly with compliance requirements, offering a secure method of handling sensitive data while sticking to data protection regulations.
This ensures that entities operating within the blockchain space can navigate regulatory frameworks with confidence and integrity.
Techniques of Data Tokenization
Secure Hash
Secure hash function is one of the most fundamental data tokenization techniques. It involves the use of cryptographic hash functions to generate fixed-length, unique strings of characters (hashes) from sensitive data.
These hashes are irreversible and become the tokens, preserving the security of the original data. Secure Hash is widely used for its efficiency and ability to maintain data integrity.
Format Preserving
Format preserving tokenization retains the format of the original data while transforming it into tokenized data, in other words, a token. This method is especially valuable when the structure of the data, such as credit card numbers, payment card data, or identification codes, needs to be preserved for later processes.
Split Tokenization
Split tokenization, as the name suggests, divides sensitive data into multiple parts, tokenizing each one separately. The tokens are then linked, and the original data can only be reconstructed when all the tokens are combined.
This approach enhances security by dispersing information, reducing the risk associated with a single token being compromised.
Randomized Tokenization
Randomized tokenization introduces an element of randomness to the tokenization process. Unlike deterministic methods, where the same input always yields the same output, randomized tokenization produces varied tokens for identical data.
This unpredictability is a good thing because it adds an extra layer of security, making it challenging for attackers to deduce patterns.
Cryptographic
Cryptographic tokenization uses advanced cryptographic algorithms to transform sensitive data into tokens. This method ensures a high level of security by utilizing encryption techniques. The tokens generated are nearly impossible to reverse engineer without the appropriate decryption keys.
Detokenization
Then there's detokenization in data security, which is the reverse process of tokenization, where tokens are converted back into their original form. This capability is crucial for authorized parties to access and utilize the tokenized data appropriately.
While the primary focus in tokenization is on securing data, detokenization ensures that legitimate users can retrieve and interpret the original information as needed.
Data Tokenization VS Data Encryption
We mentioned how cryptographic tokenization of sensitive data is similar to data encryption, but what are the differences?
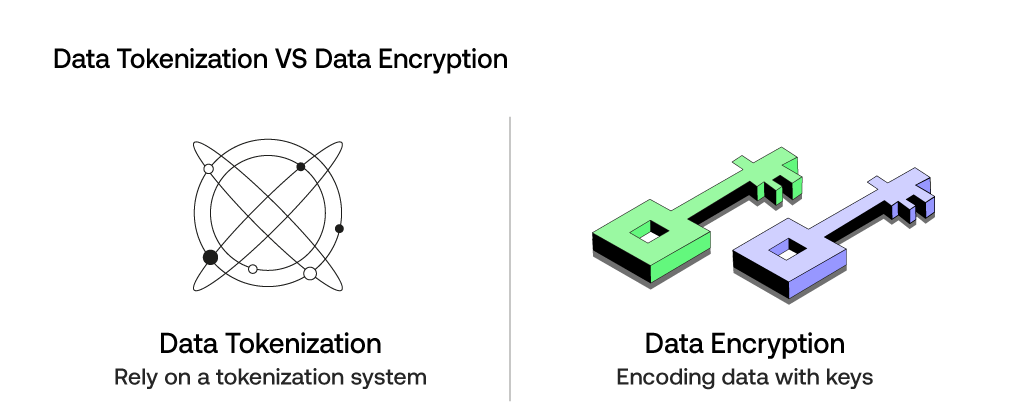
Data tokenization and data encryption are both pivotal in bolstering data security, particularly in safeguarding sensitive information like credit card data and primary account numbers. While encryption involves encoding data with a key to make it unreadable without the corresponding decryption key, tokenization takes a different approach.
In tokenization, sensitive data is replaced with unique tokens, rendering the original information indecipherable. The main difference lies in the management of keys: encryption requires secure handling of encryption keys, whereas tokenization relies on a tokenization system.
In the event of a data breach, encrypted data may remain protected as long as the encryption key is secure. However, tokenized data provides an additional layer of defense by replacing the sensitive information completely.
Pros and Cons of Data Tokenization
Pros:
- Enhanced security
- Compliance adherence
- Efficient data handling
- Simplified key management
- Minimized impact of data breaches
Cons:
- Implementation complexity
- Initial setup costs
- Token storage challenges
- Dependency on tokenization systems
Conclusion
Data tokenization has robust security measures, efficient data handling, and compliance benefits that make it indispensable in the protection of sensitive information. While challenges like implementation complexity and initial costs exist, the overall impact of data tokenization in strengthening decentralized systems and ensuring the integrity of information makes it a key player in the ongoing digital transformation.
Related Articles:
Market Makers vs. Market Takers – The Roles They Play
Best Crypto Exchanges for SecuX Wallets
Digital Signatures – What They Are and What They Do
Sources:
What is data tokenization, and how does it compare to data encryption?
0 comments