Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as financial advice.
In a world where security is paramount, symmetric and asymmetric encryption battle it out for domination. These cryptographic techniques are the foundation of secure data transmission and storage, each with its own unique strengths and applications.
They are different encryption methods, both offer security, but we know they are applied in different settings. Let’s get to know them today.
Simple Cryptography Terms
We can’t fully grasp the meaning and importance of symmetric vs asymmetric encryption without understanding basic cryptography terms.

Encryption
Encryption is the process of converting plain, readable text or data into a cryptic format using algorithms and a secret key. It aims to secure information during transmission or storage, making it difficult for unauthorized parties to access or understand the content.
The encryption process uses complex mathematical operations to scramble the data, and it can only be reversed through decryption with the appropriate key. Encryption is modern cryptography used to safeguard sensitive information in areas such as online banking, communication, and data protection.
Decryption
We mentioned decryption above, and it is the the conversion of encrypted data back into its original, readable form. Decryption is achieved by using a specific decryption key, which reverses the process of encryption.
Decryption is vital for authorized parties to access and understand encrypted information securely. Without the proper key, the encrypted data will still be incomprehensible, which protects the data. We can see decryption at the heart of secure communication, digital signatures, and various cryptographic systems.
Key
In cryptography, a key is a vital piece of information used to control the encryption and decryption of data. Keys are like secret codes or passwords. They are used with special math rules (cryptographic algorithms) to change regular text into secret code (encryption) and to change secret code back into regular text (decryption).
There are two main types of keys in cryptography: symmetric keys, where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption, and asymmetric keys, where a pair of keys (public and private) are used. The security and strength of encryption heavily depend on the secrecy and complexity of the key making.
Steganography
Steganography is a bit like hiding a secret message within something else, like a picture, music, or text. It’s a way to keep information private by making it look like there’s nothing hidden, when in fact, there is something hidden in plain sight.
Imagine writing a message on a piece of paper and then hiding that paper inside a book. To anyone else, it just looks like a regular book. Steganography comes in handy when you want to keep things confidential, especially when you don’t want others to know that you’re hiding something at all.
Symmetric Encryption Decoded
Now let’s get into the ins and outs of symmetric encryption. It is a crucial concept in the world of cryptography, in terms of safeguarding data using a single secret key. In this method, the same key is used for both encryption and decryption, making it a faster and more efficient way to secure information compared to asymmetric encryption.
The beauty of symmetric encryption lies in its simplicity. It relies on a single secret key, shared between parties that need to exchange secure information. This key is used in combination with an encryption algorithm to transform plaintext data into ciphertext, making it indecipherable to anyone who doesn’t possess the key. To read the encrypted data, one simply needs to apply the same key in reverse to decrypt it.
Symmetric encryption is known for its speed and efficiency, which makes it the leading choice for tasks such as securing files on your computer or encrypting data during a video call.
While symmetric encryption excels in terms of speed and efficiency, there are limitations. It’s primary drawback is securely sharing the secret key between parties. If not done properly, the key exchange process can be a weak point.
Symmetric encryption simplifies the process by using the same key for both encryption and decryption, and while it’s more convenient, it’s less secure than its counterpart. However, that’s not to say symmetric encryption is inferior because the right choice depends on the specific security needs of an application.
What is Asymmetric Encryption?
Asymmetric encryption, often referred to as public-key encryption is unlike symmetric encryption, where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption, asymmetric encryption employs a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. Like we mentioned, this dual-key system adds an extra layer of security to data protection.
In asymmetric encryption, the public key is widely available and can be freely distributed. It’s used for encrypting data, making it accessible only to the recipient who possesses the corresponding private key. The private key, on the other hand, must be kept secret and is used for decrypting the data back to its original form.
One of the primary advantages of asymmetric encryption is its ability to securely exchange data and establish secure communication channels without the need to exchange secret keys beforehand – a big issue in symmetric encryption. This feature makes it an excellent solution for tasks like secure email communication, online transactions, and digital signatures.
Asymmetric encryption requires more computational power than symmetric encryption, which is why the two are often used together. For example, a common use case is to establish a secure communication channel using asymmetric encryption to exchange a shared symmetric key. Communication can then use the faster symmetric encryption with the shared key for data protection.
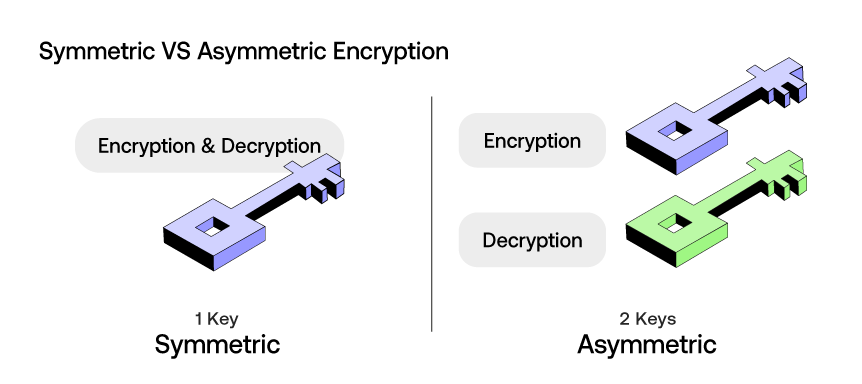
Symmetric VS Asymmetric Encryption
Symmetric Encryption:
Pros:
- Faster processing due to the simplicity of using a single key.
- Efficient for large-scale data encryption, such as bulk data transfers.
- Less computational power, making it suitable for resource-limited purposes.
Cons:
- Key distribution can be challenging as the same key is used encrypt and decrypt data.
- Vulnerable to interception during the key exchange.
- Does not provide secure communication over untrusted networks without additional protocols like VPN or TLS.
Asymmetric Encryption:
Pros:
- Secure key exchange without the need for prior key distribution.
- Ideal for secure email communication and digital signatures.
- Strong security model with a separate private key and public key.
Cons:
- Slower processing due to the use of both the private key and public key.
- More computationally intensive, which may be a limitation in resource-constrained systems.
- More complex and requires additional processing power, making it less suitable for high-volume data encryption.
Conclusion
The comparison between symmetric and asymmetric encryption highlights their unique advantages and limitations in various scenarios. Symmetric encryption relies on a single key and excels in speed and efficiency for data encryption. On the other hand, asymmetric encryption’s dual-key system provides enhanced security, particularly in securely exchanging data. Understanding when to deploy each encryption algorithm is key to safeguarding data effectively.
Related Articles
How Blockchain is Changing Payment Methods
Crypto Hash – What Is It and What Does It Do?
How to Store NFTs – Doing It Safely and Securely
Sources
Difference Between Symmetric and Asymmetric Key Encryption – GeeksforGeeks
Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Encryption – What are differences?
Types of Encryption: Symmetric or Asymmetric? RSA or AES? | Prey Blog
0 comments