
Decentralization is an important cornerstone of the web3 industry. Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies rely greatly on this factor and it has been an appealing aspect for many supporters. Decentralization is a little different in the blockchain world, with profound implications for security and governance. Whether you’re already immersed in blockchains or just getting into crypto, decentralization is a key principle to understand.
Table of Contents
- Decentralization in Blockchain and Crypto
What is Decentralization in Blockchain?
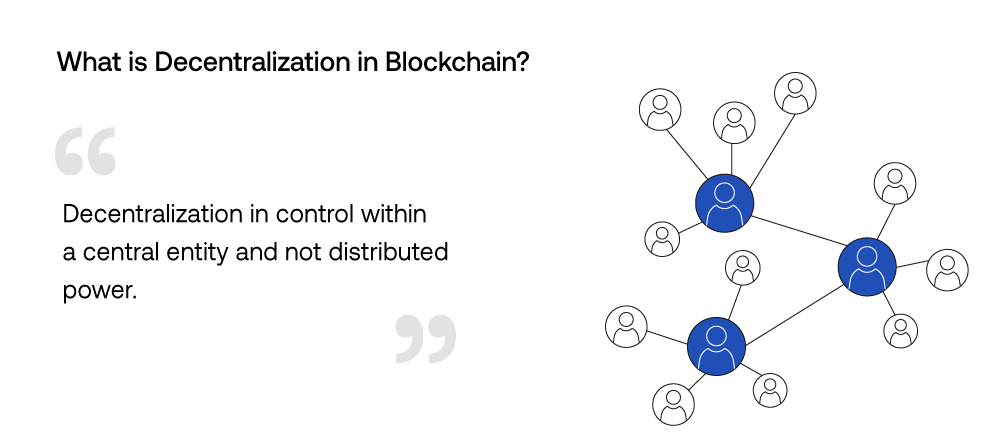
Decentralization in terms of blockchain and crypto refers to power and control being distributed among many, rather than being held by one central entity. In blockchain technology, the many in this case would be participants within a chain and nodes.
In doing so and ensuring that authority is spread among many, it provides trust within the ecosystem. A big benefit is users being able to partake in peer-to-peer transactions with more peace of mind without having to rely on intermediaries. How? Because transactions are publicly visible to the network participants and due to smart contracts, they are also immutable.
Aside from security benefits and distribution of power, a blockchain network is decentralized to also eliminate any single point of failure. If one node on the chain fails, the other network nodes will continue to operate to bolster resilience.
Blockchain technologies were conceptualized to counteract centralized systems. When we think of a blockchain network, we think about Bitcoin, the first-ever blockchain. It has played a pivotal role in paving the way for other decentralized networks, decentralized finance (DeFi), smart contracts, and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
Types of Decentralization in Blockchain Networks
There are actually a few types of decentralized networks, with the following being the most prominent:

- Architectural decentralized network
Architectural decentralization refers to the physical designs of the network. One that is of this type has multiple nodes in various geographical locations. There are many nodes in this type of decentralization and they are not confined to a single place. Every individual node will contain a copy of the entire blockchain. When a new transaction happens the nodes will work the verification process and update the chain.
A blockchain that features architectural decentralization is one that has robust security because although it may be possible for hackers to take down a single node, the entire chain is never compromised.
- Political decentralization
Political decentralization in a blockchain pertains to the authority and control within it. One that implements this type of decentralization sees control distributed among various participants in the chain or entities. In the blockchain world, this means decision-making power is held by many people.
- Logical decentralization
Lastly, we have logical decentralization. This is in reference to how data is structured within the network. It can be said that logical decentralization is at odds with architectural decentralization. We see each node having a copy of the entire network in architectural decentralization, but for the logical type, the data is broken down into separate parts that function as a whole.
While at the moment there isn’t a blockchain that is fully logical, the closest we can see in a network that is taking a step towards this type of centralization is Ethereum 2.0 and its sharding scalability solution.
It’s possible to see both political and architectural decentralization in a single blockchain. Ethereum and Bitcoin are examples of this. It’s
Pros and Cons of Decentralized Networks
Do the pros outweigh the cons of a decentralized blockchain network?
Pros
- Network security
- User trust
- Transaction transparency
- Blockchain resilience
- More individual control
Cons
- User conflict
- Volatility in crypto prices
Examples of Decentralization in the Crypto World
Bitcoin and Ethereum
As the very first blockchain, the Bitcoin network has become a pioneer in web3. It paved the way for the likes of Ethereum to take decentralization even further with smart contract and decentralized application (dApp) development.
DeFi
Decentralized finance leverages Ethereum’s smart contracts to function as a traditional financial system would – without the centralized entity. There are platforms for yield farming, staking, liquidity pools, lending, and borrowing cryptocurrency.
DAOs
DAOs are led by the voting power of their members and are groups that operate without a central entity. The structure of DAOs is helpful to run businesses, manage funds, and act as decision-makers.
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs)
For lending crypto, we have decentralized exchanges or DEXs. They work much like a centralized exchange would – but without the central power.
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs)
NFTs took the world by storm a few years ago (thanks Bored Ape and CryptoPunks) and made some of the holders millions. Each NFT is unique and is used to represent ownership of either a digital or real-world asset. NFTs are an example of decentralization because they are bought, traded, and sold on decentralized marketplaces such as OpenSea.
Implications of Decentralization in Technology
What implications does decentralization have in technology, and how can bring on a revolutionary change within the next decade?
Decentralization will have a lasting impact on finance, as web3 supporters witness every day in crypto, and it brings on new forms of decentralized governance with the distributed network.
Privacy and security are also enhanced as there is less data being controlled by a central authority, which means fewer data breaches and compromisation. As we see in NFTs, content creation could also spread to other industries and we see more interoperability between platforms with the introduction of decentralized technology.
We’ve only just begun to scratch the surface of what a decentralized blockchain can do for our society.
Conclusion
Decentralization can really be seen as a paradigm shift in control. Removing a single entity with full control over decisions really puts the power back into the hands of the people. However, this utopia isn’t without drawbacks, but as decentralized blockchain technology grows, so do advancements and solutions to remedy any risks.
Related Articles:
- What Are Blockchains and the Tech Behind Them?
- DApp Connect – Adding More Value to Your Crypto Wallet
- The MetaMask QR Code – Why We Need It
0 comments